
It is one of the most commonly used inter-dependency techniques and is used when the relevant set of variables shows a systematic inter-dependence and the objective is to find out the latent factors that create a commonality. It may help to deal with data sets where there are large numbers of observed variables that are thought to reflect a smaller number of underlying/latent variables. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, personality psychology, biology, marketing, product management, operations research, finance, and machine learning. Ī common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. PSPP, SAS, Stata, STATISTICA, JMP and SYSTAT.
#Pspp factor analysis plus#
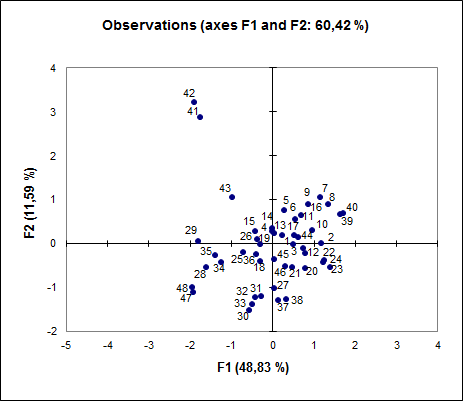
The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus " error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. To conduct a factor analysis, click the 'Analyze' drop-down menu then choose the Factor Analysis option as shown in figure 4-11 below. Factor analysis is related to principal component analysis (PCA), but the two are not identical. The VARIABLES subcommand is required (unless the MATRIX IN subcommand is used). We select the KMO and Bartlett’s test of sphericity.
#Pspp factor analysis how to#
It may be used to find common factors in the data or for data reduction purposes. PowerPoint: Exploratory Factor Analysis Menu Have a look at the below slides, which illustrate how to run an EFA: Chapter Eight Exploratory Factor Analysis Menu For this test, the statistical program used was Jamovi, which is freely available to use. It can perform descriptive statistics, T-tests, linear regression, measures of association, cluster. To produce plain text output, specify -o file on the PSPP command line, optionally followed by options from the table below to customize the output format. The FACTOR command performs Factor Analysis or Principal Axis Factoring on a dataset. PSPP is a program for statistical analysis of sampled data. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. PSPP can produce plain text output, drawing boxes using ASCII or Unicode line drawing characters. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables.
For factorial design, see Factorial experiment.įactor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. Based on psychometric, theoretical, cross-cultural, and practical considerations, the results support the use of the PSDQ in a wide variety of research and applied settings.This article is about factor loadings. (1994) with Australian high school students. Results based on this study with Turkish university students largely replicate and extend the findings of Marsh et al. However, support for the PSPP was undermined by extremely high correlations among several of its factors, due in part to a substantial method effect associated with its idiosyncratic response scale. In support of construct validity interpretations, matching PSDQ and PSPP factors were highly correlated. The sample, 1,041 Turkish university students in elective physical education courses from 10 Turkish universities, provided a test of the cross-cultural generalizability of responses to these two widely used English language instruments.


The present investigation demonstrated cross-cultural support for convergent and discriminant validity of the Physical Self-Description Questionnaire (PSDQ) in a multitrait-multimethod analysis of relations with responses to the Physical Self-Perception Profile (PSPP).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
